How Do Search Engines Work?
How Do Search Engines Work – This guide offers an introduction to how search engines function. They focus on the processes of crawling and indexing, as well as concepts like crawl budget and PageRank.
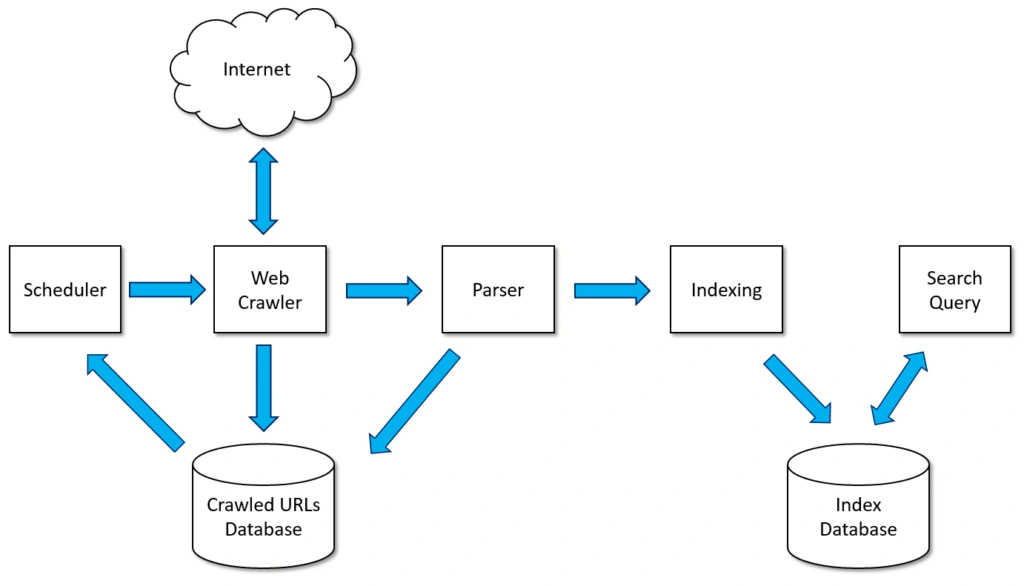
Search engines operate by crawling and indexing vast quantities of web pages. They use their own web crawlers known as bots or spiders. These web crawlers navigate the web by downloading web pages and following the links on these pages. This makes them to discover new content as it becomes available.
Search engine index
When search engines discover web pages, they add them to a data structure called an index. This index is a repository that contains all the URLs the search engine has found, along with several key signals about the content of each page.
The index includes information such as:
- Keywords within the content: The search engine identifies the main topics and subjects covered in the page by analyzing the keywords within the content. This helps the engine understand what the page is about and match it to user search queries.
- Type of content: Search engines assess the type of content on a page using microdata like Schema markup. This metadata helps categorize the content and understand the page’s purpose. YThis includes as whether it’s an article, product, review, or other types of content.
- Freshness of the page: Search engines track how recently a page was updated, as fresher content is often more relevant to users. Keeping content up-to-date helps improve its visibility in search results.
- User engagement: Search engines analyze how users interact with a page and the domain it belongs to. High levels of engagement, such as time spent on the page, click-through rates, and social shares, signal that the content is valuable and relevant to users.
By compiling this information in the index, search engines can efficiently retrieve the most relevant pages for a user’s search query. The process of crawling and indexing allows search engines to create a comprehensive map of the web, enabling them to deliver accurate and useful search results to users. Understanding these factors can help website owners optimize their content for better visibility and engagement.
Why Do I Need Search Engine Algorithm?
The goal of a search engine algorithm is to quickly deliver a relevant set of high-quality search results that accurately answer the user’s query.
Once the user selects an option from the search results and engages with the content, this interaction and subsequent actions contribute to future learnings that can influence search engine rankings over time.
What happens when a search is performed?
When a user enters a search query into a search engine, the search engine identifies all relevant pages from its index and uses an algorithm to rank them in order of relevance, presenting a set of results to the user.
The algorithms that determine the ranking of search results vary between search engines. For instance, a page that ranks well for a particular query on Google may not have the same ranking on Bing.
In addition to the search query, search engines also take into account other data to deliver results:
- Location: Some queries are location-specific, such as “cafes near me” or “movie times,” so the search engine tailors results based on the user’s location.
- Language Detection: If the search engine can detect the user’s language preference, it will return results in that language.
- Previous Search History: The search engine may adjust the results for a query based on the user’s prior search history.
- Device: The results can vary depending on the device used to perform the query. So as search engines aim to optimize results for the user’s specific device.
What makes a page not be indexed?
There are several reasons why a URL might not be indexed by a search engine:
- Robots.txt File Exclusions: This file specifies which parts of your site search engines should avoid crawling.
- Webpage Directives: Directives such as a “noindex” tag tell search engines not to index a page, while a “canonical” tag points search engines to a preferred, similar page to index instead.
- Quality Judgments: Search engine algorithms may determine that a page is of low quality, contains thin content, or is duplicative, resulting in it not being indexed.
- Error Pages: A URL may not be indexed if it returns an error page, such as a 404 Not Found HTTP response code.